Exocrine Pancreatic Insufficiency
Know the gastric symptoms of exocrine pancreatic insufficiency
A person with EPI may experience symptoms similar to those of several other digestive conditions, which can sometimes make it difficult to recognize.
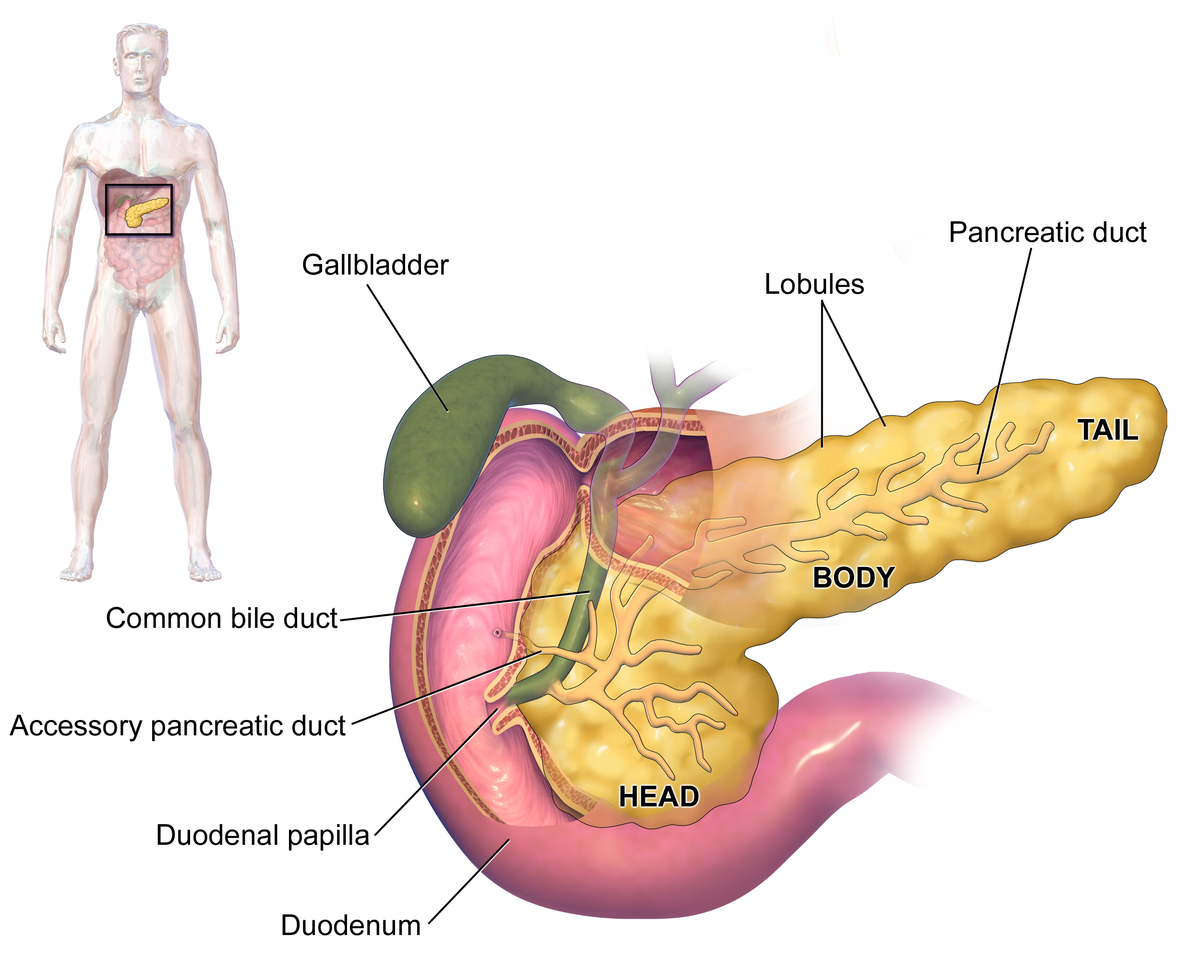
Overview
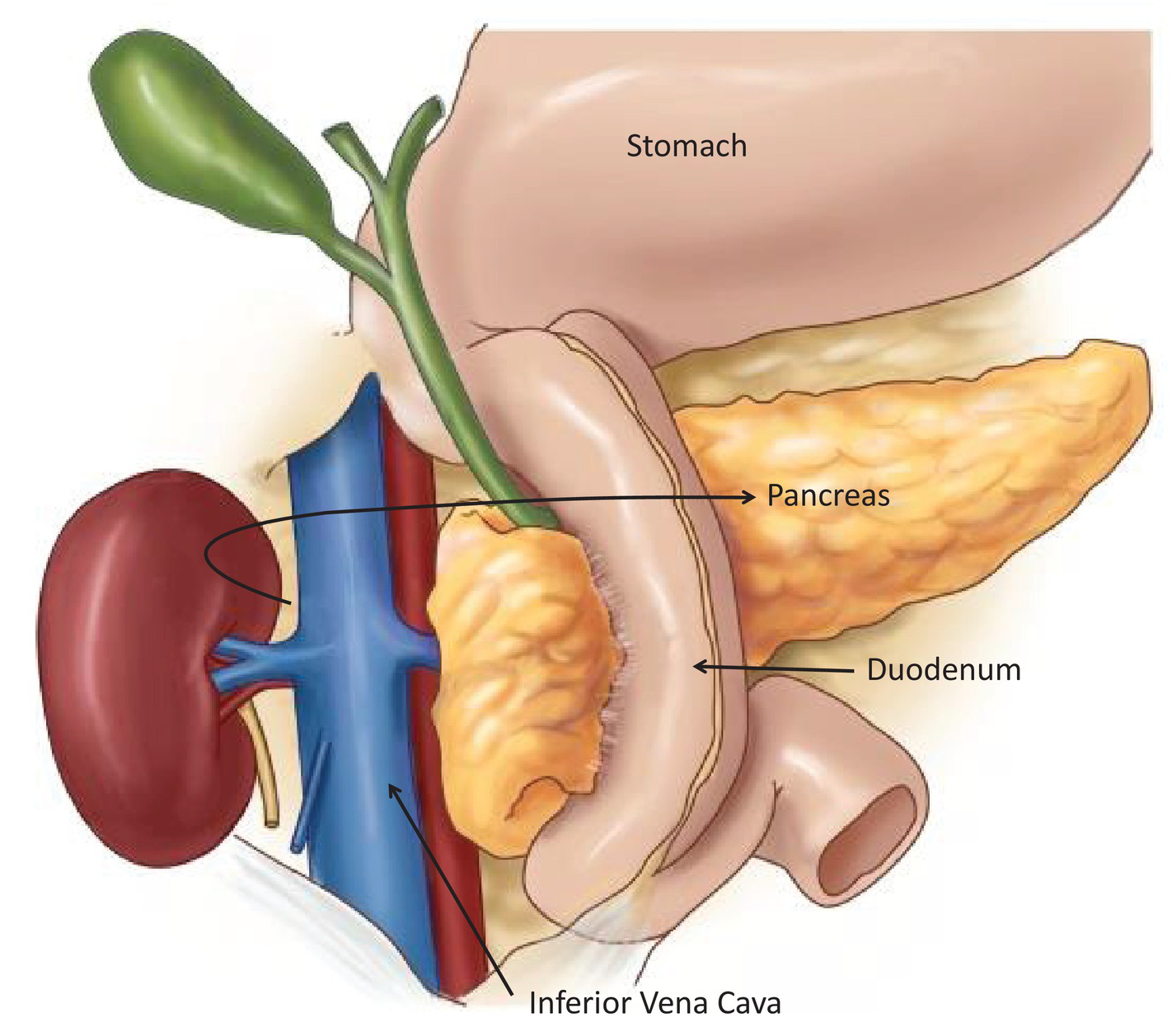
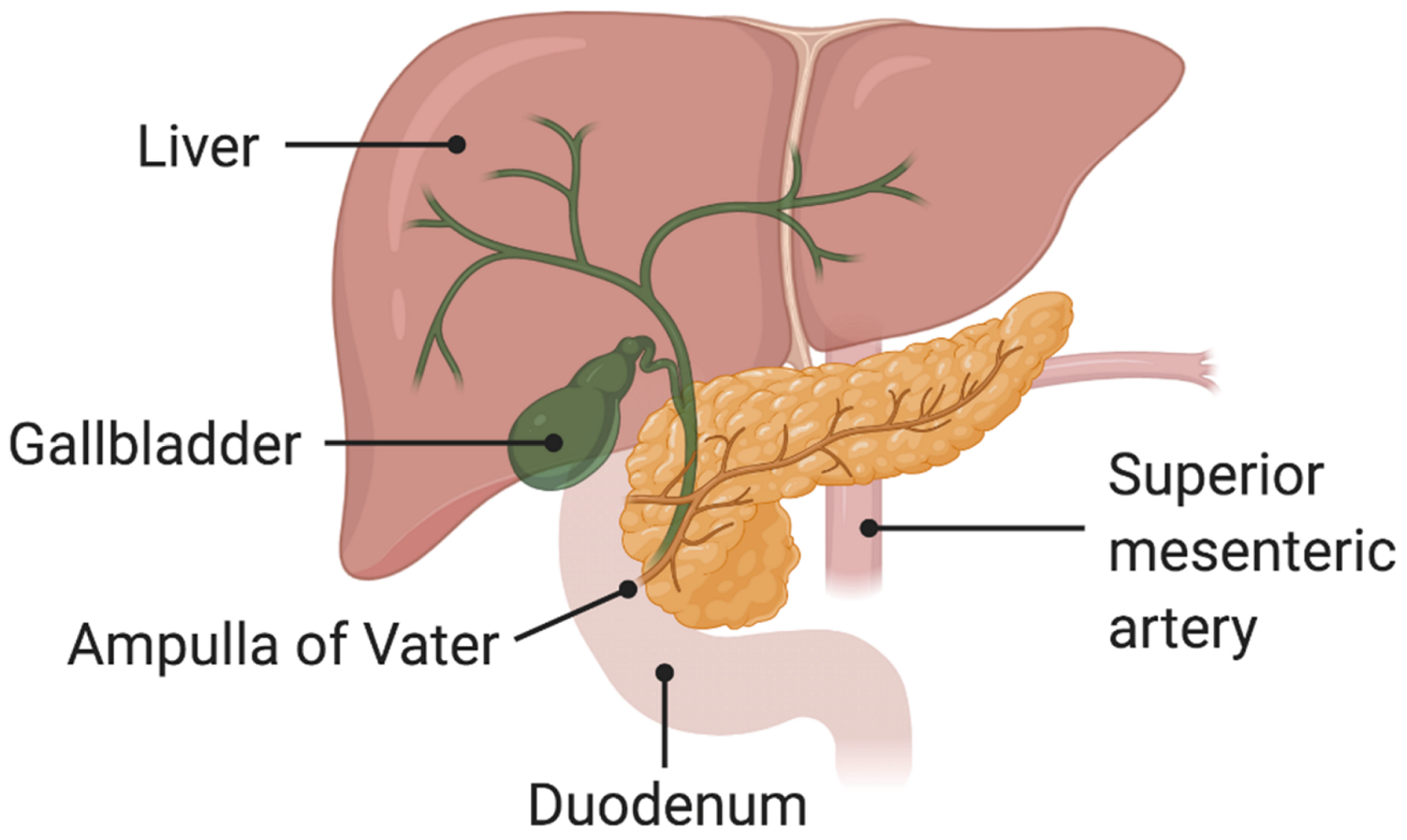
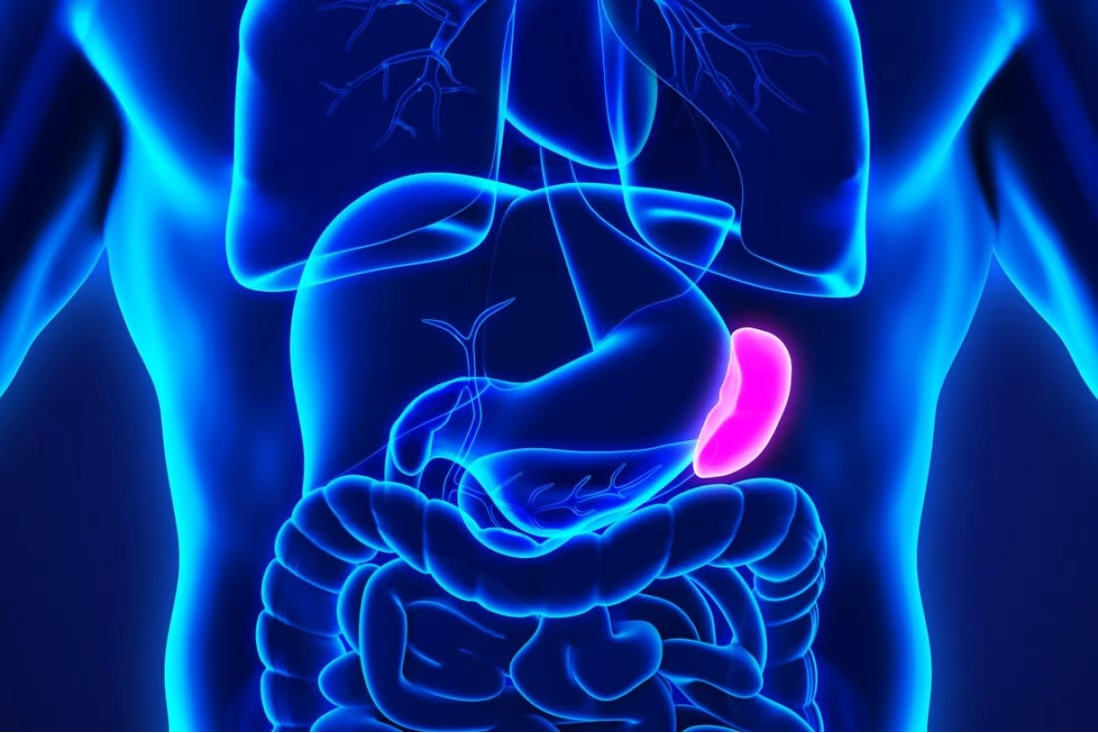
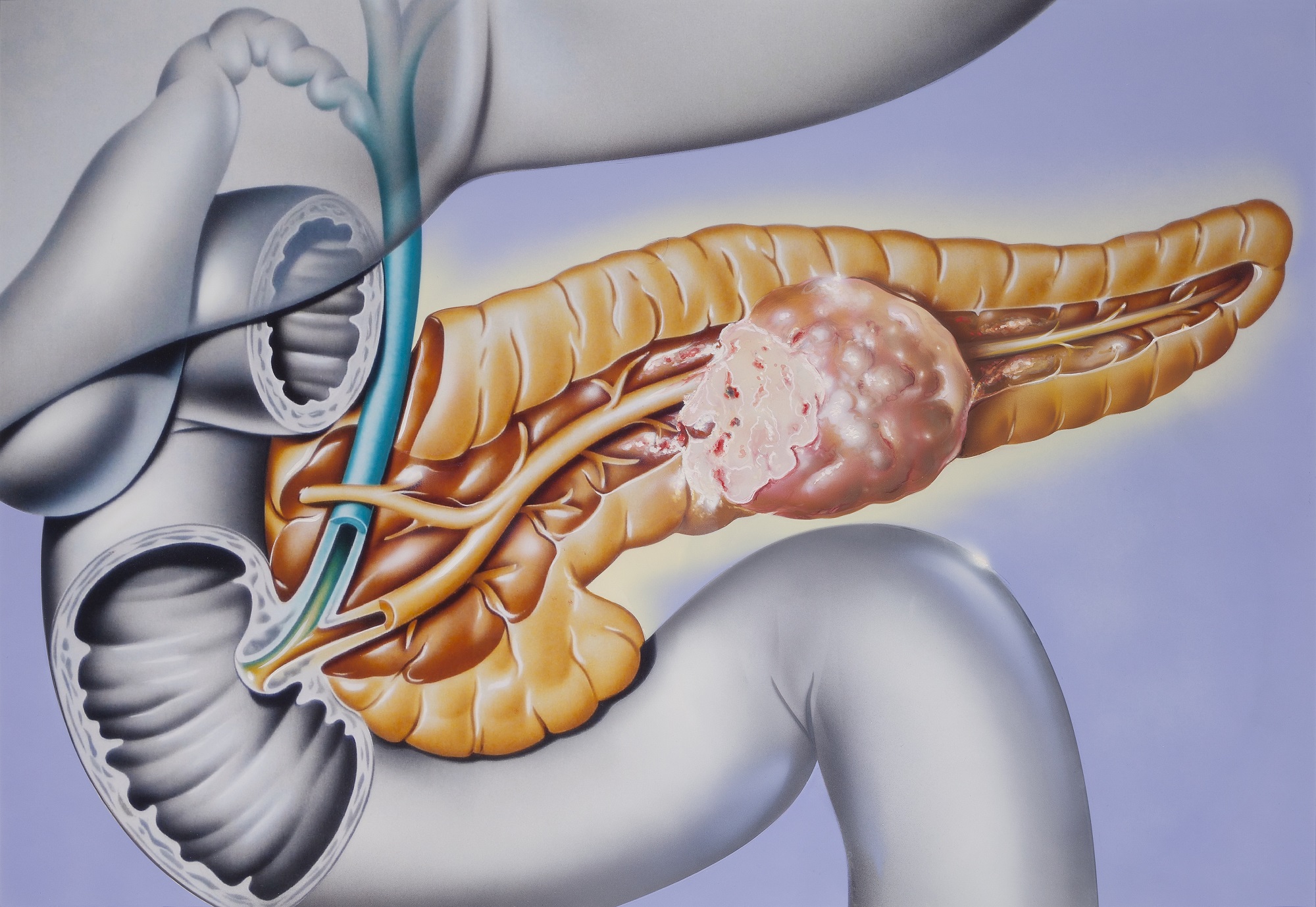
The pancreas plays an important role in digestion. It produces enzymes that help break down carbohydrates, fat, and protein, allowing the body to get the nutrients it needs to function.
Damage to the cells that produce these pancreatic enzymes can cause EPI. In people with the condition, the pancreas does not produce enough enzymes for the body to break down food and absorb nutrients.
Experts do not know how many people are living with EPI. (Source)
As EPI makes it difficult to digest food, a person with the condition may experience various digestive symptoms, such as:
- Bloating
- Gas
- Abdominal pain
- Fatty stools
Without treatment, the condition can lead to several complications, such as malnutrition, bone problems, and reduced life expectancy. People who receive treatment will likely experience a general improvement in their symptoms, but they may still require nutritional supplements to avoid malnutrition. (Source)
Digestive symptoms of EPI
In people with EPI, the body does not break down carbohydrates, proteins, and fats in foods into substances that it can absorb. As a result, undigested and unabsorbed food remains in the digestive tract, which can lead to a number of uncomfortable gastrointestinal symptoms.
The symptoms of EPI are generally nonspecific. In other words, a person or their doctor may not immediately recognize EPI as the cause of the symptoms. (Source)
Steatorrhea
Steatorrhea refers to excess fat in the stool. It is the most common sign of EPI. (Source)
A doctor can test for excess fat in the stool using a 72-hour stool test. They will diagnose steatorrhea if the stool contains 7 grams (g) or more of fecal fat in a 24-hour period while eating a diet that includes 100 g of fat a day. (Source)
Steatorrhea often causes stool that is:
- Bulky
- Pale
- Loose
- Bad-smelling
- Oily or greasy
- Hard to flush
Although EPI often causes steatorrhea, there are other possible causes, including medication side effects.
Other symptoms of EPI
People with EPI may experience unexplained weight loss because the body cannot absorb nutrients. They may also experience nutritional deficiencies, particularly of the fat-soluble vitamins A, D, E, and K.
Other common digestive symptoms of EPI include:
- Abdominal pain
- Bloating
- Excess gas
- Diarrhea
It is important to note that these symptoms do not necessarily mean that a person has EPI. Other conditions can also produce these symptoms. A person should speak with a doctor if they develop persistent gastrointestinal symptoms or suspect that something may be wrong.